Coagulation and Flocculation Meaning: Key Concepts in Water Treatment
What is Coagulation?
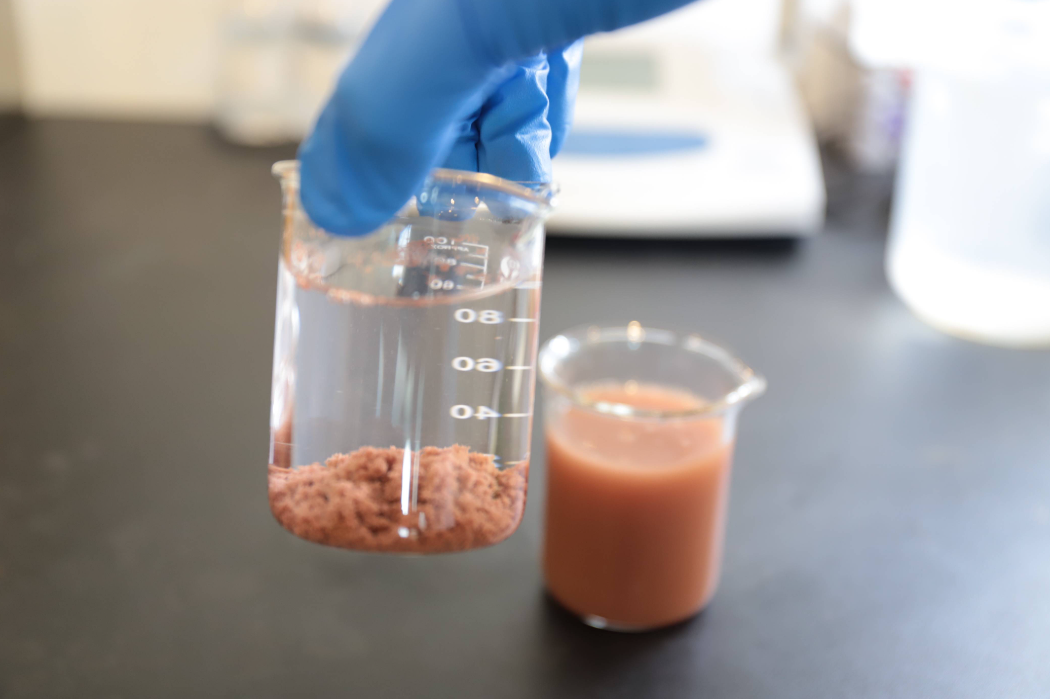
Coagulation is the process of adding chemicals to water to destabilize suspended particles and colloids. These particles usually carry negative charges, which prevent them from coming together and forming larger clusters. By introducing coagulants, such as aluminum sulfate or ferric chloride, the negative charges are neutralized, allowing the particles to bond.
In water treatment plants, coagulation is a critical first step to ensure that impurities are removed efficiently. This process is often paired with flocculation to maximize its effectiveness.

Understanding Flocculation
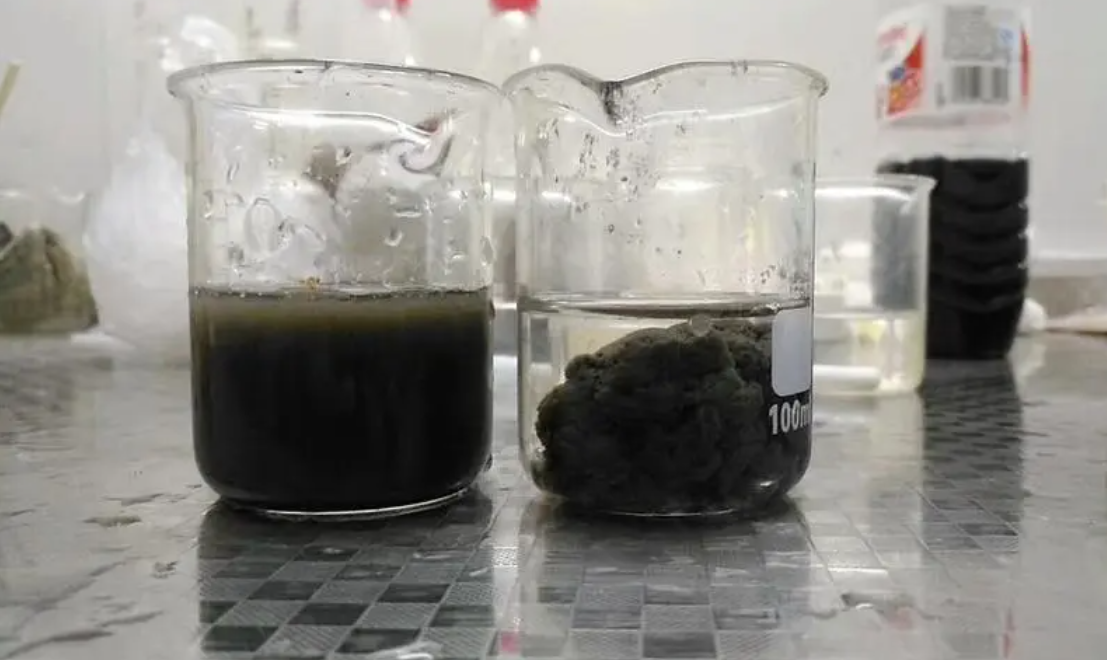
Flocculation is the next step in the water treatment process after coagulation. It involves gently mixing the water to encourage the formation of larger aggregates, known as flocs. These flocs are easier to separate from the water through sedimentation, filtration, or other methods.
The process is typically aided by flocculants, which are substances that help bind the particles together. Flocculation ensures that even the smallest impurities are removed, resulting in cleaner, safer water for consumption and industrial use.
The Importance of Coagulation and Flocculation in Water Treatment
Coagulation and flocculation are essential processes in water treatment because they address the removal of suspended solids, organic materials, and even certain microorganisms. Without these steps, it would be nearly impossible to achieve the clarity and purity required for safe drinking water or industrial applications.
By integrating these techniques, water treatment facilities can reduce turbidity, improve filtration efficiency, and meet stringent regulatory standards. The combined power of coagulation and flocculation ensures that water is not only clear but also free of harmful contaminants.
How Do Coagulation and Flocculation Work Together?
Coagulation and flocculation are complementary processes that work hand-in-hand. Coagulation prepares the particles by neutralizing their charges, while flocculation encourages them to come together into larger clumps. These larger clumps, or flocs, can then be removed through various separation techniques.
Think of coagulation as the “unlocking” stage that destabilizes particles and flocculation as the “assembling” stage that binds them into removable clusters. Together, these processes form the backbone of effective water purification systems.
Conclusion
Coagulation and flocculation are indispensable in modern water treatment. By understanding their meanings and functions, we can appreciate the science behind clean, safe water. Whether you’re a student, an industry professional, or simply curious about water purification, knowing how coagulation and flocculation work will deepen your understanding of this vital process.
Remember, clean water isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Coagulation and flocculation play a crucial role in making it possible.